Mould is a type of fungal organism that can be found both indoors and outdoors. So is present everywhere and part of our everyday environment. It can grow on almost any surface, and there are thousands of different types of mould.
Some types are harmless, while other types can cause problems. Let’s look more at what mould is, and why it can be useful to know about it.
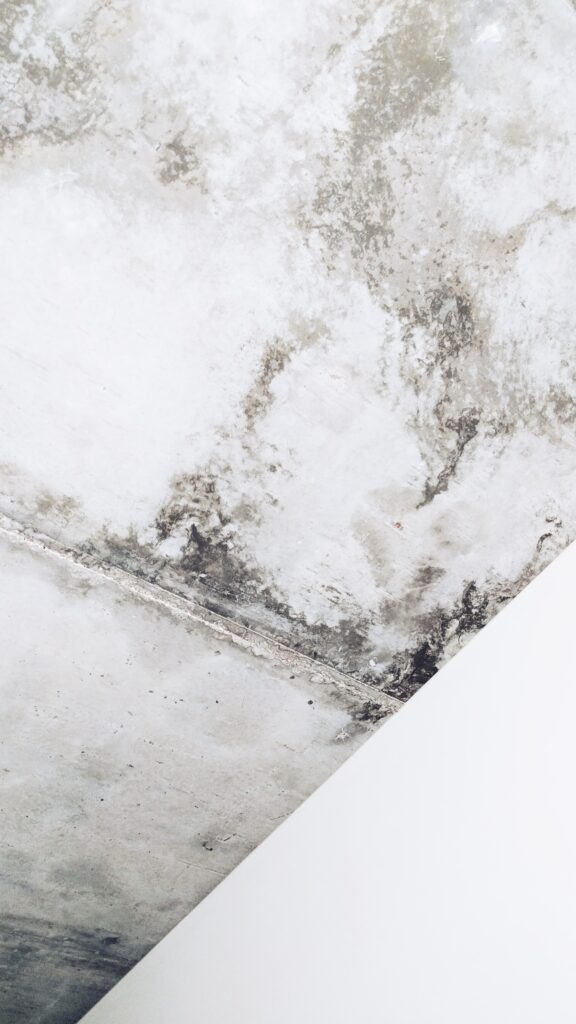

The mould-story
Mould is a type of fungi that grows best in damp, dark, and humid conditions. It is common in gardens, amongst rotting leaves, and in the soil.
It reproduces through tiny spores that are released into the air. When these spores land on a suitable surface, they begin to grow and form new colonies. It is through these spores being blown in, or carried in by us or our pets that mould spores are naturally occurring indoors too.
They play an important role in the ecosystem, particularly by breaking down dead organic matter. However, it can also cause problems for humans when it begins to multiply and accumulate in places where people live and work. This creates a conflict between us and them. In these situations it exerts harmful effects by, alongside its spores, releasing harmful toxins into the air that can cause respiratory problems, allergic reactions, and other health complications. The amount of mould can also damage building structures.
This fungus has been around for millions of years. Its evolution has been shaped by its environment and the organisms it interacts with. For example, the development of spore-producing structures was likely an adaptation to help mould survive in dry conditions. Today, it continues to evolve and develop in response to changing conditions on Earth. As our understanding of this fascinating organism continues to grow, we may be able to find new ways to harness its power and manage its harmful effects to co-exist together.
What does mould look like?
This fungus can grow in many different environments, although commonly in damp areas. It can be white, black, green, or blue, and it often has a fuzzy, powdery or slimy appearance.
Microscopically, mould is made up of tiny spores that are invisible to the naked eye. These spores are what allow mould to reproduce and spread. They can be released into the air when the mould is disturbed. They also disperse as part of its natural growth and spreading behaviour.
Where can you find it?
As with other types of fungi, mould is very common in nature. There are an estimated 100,000 different types of mould. They can be found almost anywhere, having adapted to a wide range of environmental systems. While mould is often associated with decay, it can be found in many different types of environments, including forests, caves, and even Antarctica. In nature, it typically grows on dead organic matter, such as fallen leaves or dead animals. However, it can also grow on living things, such as plants.
Overall characteristics include that it grows best in warm, humid conditions. Dampness, along with oxygen and an organic food source and some warmth trigger the spores to grow.
The benefits of mould
Mould is often seen as a nuisance, but it can also have some beneficial uses.
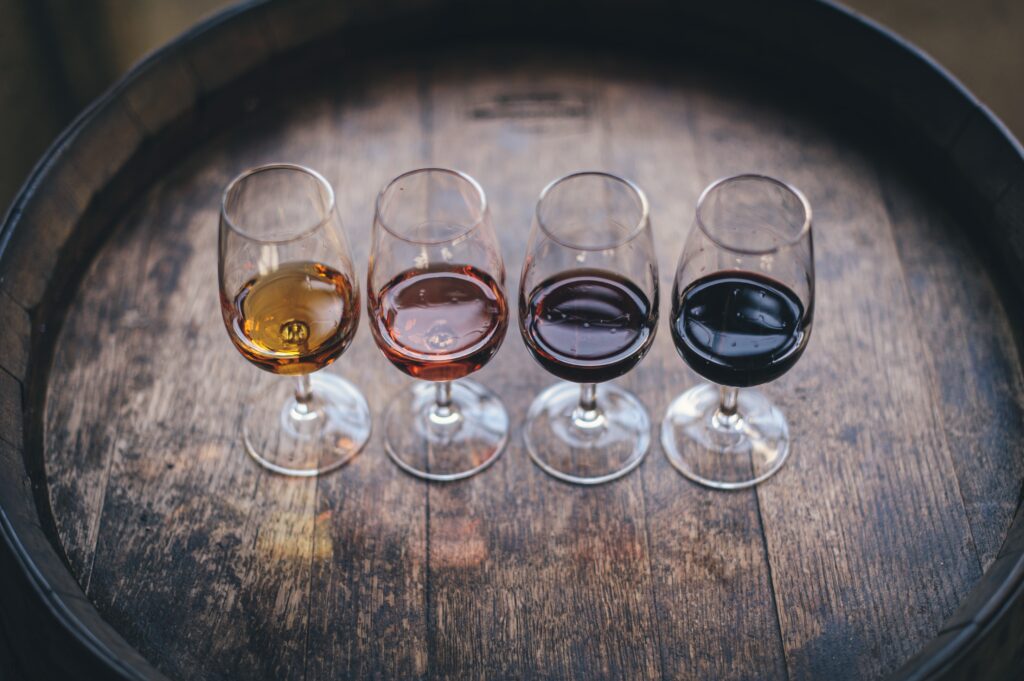

- Some types of mould have been used in the production of cheese and soy sauce for centuries. Mould is a necessary part of the wine-making process. It helps to break down the grape skins and release the flavourful compounds inside. Grapes left to develop a special kind of mould can have some impressive benefits. This specific mould, called Botrytis cinerea, can result in the development of a sweet and viscous wine known as a “Sauternes.” The concentrated sugars and flavours developed by the Botrytis cinerea mould are highly prized by wine enthusiasts around the world.
- Mould is also an important part of the ecological decomposition process. It helps to break down dead organic matter and recycle nutrients back into the environment for plants and other organisms.
- Other types produce antibiotic-like substances that can help to protect plants and animals from harmful bacteria.
- Some moulds produce metabolites that are toxic to certain types of pests but are harmless to other organisms.
- Certain moulds have been found to produce compounds that can be used in the production of biofuels or pharmaceuticals.
Why it becomes a problem
A problem organism causes harm to people, animals, or plants. Many different types of organisms have potential to become problem, and the circumstances that cause them to become a problem vary from case to case.
Some theories about why the mould organism has developed to become a growing problem in modern life include:
- The increase in airtight buildings, homes, vehicles and other systems of day-to-day life.
- A global change in climate patterns, many of which favour mould growth.
- Effects of the widespread use of chemicals and potent medications, and
- Pollution
- Lifestyle habits that make us more likely to come into conflict with mould include:
– smoking
-having homes too warm and damp
-abandoned/neglected spaces within and outside the home
-too much stuff in storage
-reluctance to ventilate spaces adequately
- Similarly, a steady increase in various diseases and disorders, also makes us more susceptible to its actions.
Because mould thrives in warm, moist environments, it tends to grow more rapidly in bathrooms, kitchens, basements. Also, in other areas where regular significant moisture is present. It is in these settings that it can accumulate to levels where it impacts the health of people and animals. Also, it can undermine the safety and structure of buildings and equipment. Some types of mould produce spores and toxins (Mycotoxins) that can cause respiratory problems, skin irritation, and other more complex health issues.
Reasons why knowing about this fungus could be helpful
1. Mould can cause significant health problems, including respiratory issues, skin irritation, and allergies ranging from mild to severe, sometimes life-threatening.
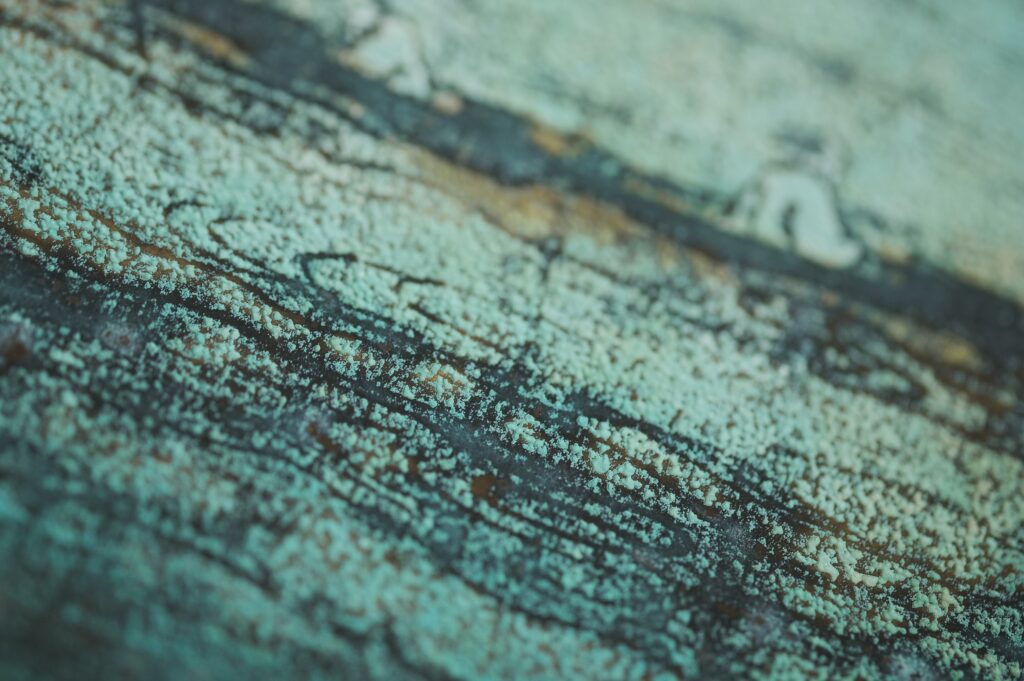

2. It can damage property, including walls, ceilings, furniture, and clothing.
3. Sometimes it can be difficult to remove completely and come back again and again to cause problems.
Lack of awareness about its presence, nature and potential to become a challenging problem is a significant factor facilitating its gaining prominence in your life and the lives of your family, friends, colleagues and community.
While this fungus occurs naturally in the environment and is all around us, it is useful to know about mould so that we can recognise if and when it becomes a problem. Learning how to manage it to live with and alongside it is important for everyone. Knowledge is power, so keep learning to be prepared.
So recognise that mould is naturally present in our environment and plays an important role in our ecosystem alongside bringing us other benefits.
Although certain types of mould and their behaviours can be harmful to humans, it is important to remember that interacting with it in some way is natural and generally unavoidable.
By understanding mould and its effects, you can take steps to limit its negative impact on your health, well-being and everyday life. Learning about mould can help you to recognise its presence in our homes and workplaces, and empower you to make informed decisions about how to deal with it in the best way.